
This matches with any of the child nodes of the "div".Īddress and Asterisk selects any attribute of the given matches any of the div nodes that contain at least one attribute of any type. It selects any element present in the node The current node is input so that it will select the parent, i.e., "div". It will select the parent of the current node. It selects the parent of the current node. It will give the currently selected node, i.e., h3. It will select the input node present anywhere in the DOM.Īddress sign selects a particular attribute of the will select all the elements which have text attribute. Additionally, it doesn't have to be the exact next node and can be present anywhere in the DOM.

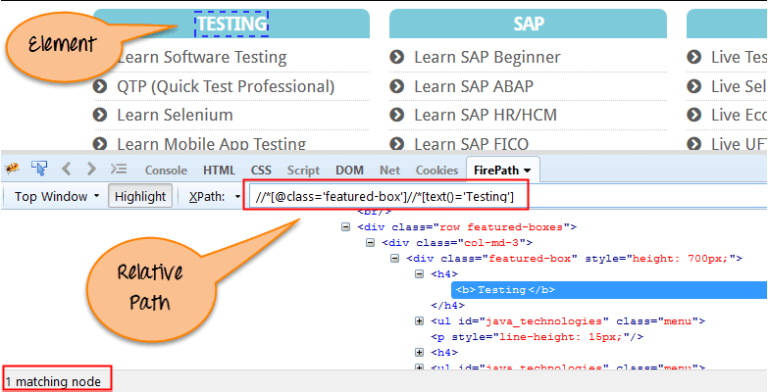
It selects any element in the DOM that matches the selection. It will look for the HTML element at the start of the document. In other words, if you want to select the first available node, this expression is used. But did you notice some special characters like double slash "//" and that help us to locate and select the desired node/element? Apart from the" //" and " provides various other syntax elements and attributes to locate the web elements using XPath. In the previous section, we learned about the basic syntax of XPath.
#FMINER RELATIVE XPATH HOW TO#
How to locate web elements using XPath in Selenium? So, this way, we can see that all the HTML pages are internally represented as an XML document and constitute the XML DOM (Document Object Model). One thing that we can notice here is every node that opens is again closed by using forward slash before the tag name, such as the tag is closed using. Similarly, the child node of the also has its own set of attributes and values. Further, you can also see the first tag has an “ id” attribute, which has a value “ app”. Here again has a child node like, which has its child nodes. It starts with a tag which has two child nodes and. For example, if we open the Chrome Dev tools section by right-clicking on the page " " and selecting the " Inspect" option, the HTML structure will look as follows: Additionally, the XML document has a tree-like structure, where we have different tags and attributes. Subsequently, let's first understand what XML DOM is and how a web page relates to an XML structure: What is HTML/XML DOM?Īll the HTML web pages are internally represented as an XML document. We will learn more about XPath and write better XPath expression as we move ahead with the tutorial.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
